Liberia Results Report 2020-2022
- Action Plan: Liberia Action Plan 2020-2022
- Dates Under Review: 2020-2022
- Report Publication Year: 2023
Government agencies’ limited funding and commitmentOGP commitments are promises for reform co-created by governments and civil society and submitted as part of an action plan. Commitments typically include a description of the problem, concrete action... resulted in a low level of implementation and few early open government results from Liberia’s fourth action planAction plans are at the core of a government’s participation in OGP. They are the product of a co-creation process in which government and civil society jointly develop commitments to open governmen.... However, modest progress was made toward establishing systems to disclose public contract and beneficial ownershipDisclosing beneficial owners — those who ultimately control or profit from a business — is essential for combating corruption, stemming illicit financial flows, and fighting tax evasion. Technical... More information. Coordination among government, civil society, and international partners was a key ingredient for these reforms.
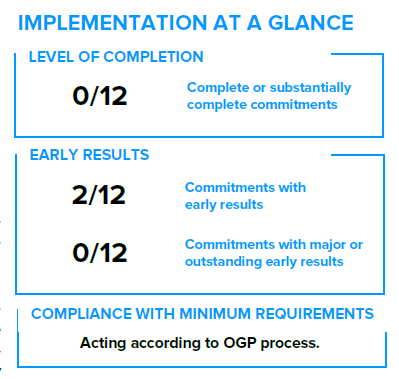
Early ResultsEarly results refer to concrete changes in government practice related to transparency, citizen participation, and/or public accountability as a result of a commitment’s implementation. OGP’s Inde... More
Liberia’s fourth action plan continued anti-corruption efforts established under previous plans. The country made modest progress toward transparency of government contracts and beneficial owners of companies. These reforms represent two of the five commitments highlighted as promising in Liberia’s Action Plan Review.[1]
Financial constraints and leadership turnover inhibited implementation of the three other commitments identified as promising, continuing challenges seen in previous action plans. Leadership challenges particularly impacted the Liberia Anti-Corruption Commission, responsible for Commitment 4, which aimed to pass long-awaited anti-corruption legislationCreating and passing legislation is one of the most effective ways of ensuring open government reforms have long-lasting effects on government practices. Technical specifications: Act of creating or r.... The Ministry of Health had taken initial steps to establish and train County Health Boards under Commitment 6. However, the boards were limited to five counties and had not yet become operational by the time of assessment.
The marginal early results achieved under Commitments 1 and 5 on open contractingA transparent procurement process, known as open contracting, increases competition, improves public service delivery, and ensures governments better value for their money. Technical specifications: C... More and beneficial ownership transparencyAccording to OGP’s Articles of Governance, transparency occurs when “government-held information (including on activities and decisions) is open, comprehensive, timely, freely available to the pub... More were facilitated by strong ownership by the respective lead agencies and technical and financial support from civil society, government, and international partners. Reformers continued to build toward the necessary institutional and legal frameworks for beneficial ownership and open contracting. However, the reformers had not achieved their overall objective to disclose new information to the public by the end of the implementation period.
CompletionImplementers must follow through on their commitments for them to achieve impact. For each commitment, OGP’s Independent Reporting Mechanism (IRM) evaluates the degree to which the activities outlin... More
Half of the 12 commitments are carried over from the previous action plan and continue Liberia’s focus on fighting corruption through open government. New policy areas included opening healthcare management, transparent taxPlacing transparency, accountability, and participation at the center of tax policy can ensure that burdens are distributed equitably across society. Technical specifications: Commitments related to c... revenue management, youthRecognizing that investing in youth means investing in a better future, OGP participating governments are creating meaningful opportunities for youth to participate in government processes. Technical ... More protection of civic space, and fighting gender-based violenceReforms that combat gender-based violence are essential for fostering an inclusive society and government that respects human rights and promotes gender equality. Technical specifications: Commitments... More.
The level of completion was lower than that of the previous action plan. Of the twelve commitments, seven achieved a limited level of completion and four were not started. These include commitments related to access to justiceAccessible justice systems – both formal and informal – ensure that individuals and communities with legal needs know where to go for help, obtain the help they need, and move through a system tha... More, citizen participationAccording to OGP’s Articles of Governance, citizen participation occurs when “governments seek to mobilize citizens to engage in public debate, provide input, and make contributions that lead to m... More in the legislature, preventing gender-based violence, and youth protection of civic space. In the case of commitments by the legislature and the Ministry of Youth and Sports, the absence of a dedicated point of contact indicates a lack of ownership by the implementing agency. Despite attempts to reach the commitment point of contact, the Independent Reporting Mechanism (IRM)The Independent Reporting Mechanism (IRM) is OGP’s accountability arm and the main means of tracking progress in participating countries. The IRM provides independent, evidence-based, and objective ... did not receive sufficient evidence on Commitment 8 on transparent tax revenue management to assess completion.
Half of the commitments were assessed as having a marginal impact on open government practices. Commitments 1 and 5 are analyzed in-depth in this report, as they represent national priorities and build toward ambitious long-term open government reforms. The remaining commitments that achieved marginal early results, such as Commitment 4 on anti-corruption legislation and Commitment 6 on transparent and participatory healthcare management, made modest progress without significant early results visible by the end of the implementation period. Under Commitment 12, iLab and the Open Government PartnershipThe Open Government Partnership (OGP) is a multi-stakeholder initiative focused on improving government transparency, ensuring opportunities for citizen participation in public matters, and strengthen... More (OGP) Liberia Secretariat monitored the government’s COVID-19 response, but the IRM did not find evidence on the impact or use of this information.
The remaining six commitments are assessed as having no early results to report yet. As detailed in the Annex, obstacles to implementation included limited funding, a lack of ownership by the responsible agency, and administrative turnover. The overall level of open government results is similar to that of the previous action plan.
Participation and Co-Creation
The Liberian OGP Secretariat works with the Steering CommitteeThe Steering Committee is OGP’s executive decision-making body. Its role is to develop, promote and safeguard OGP’s values, principles and interests; establish OGP’s core ideas, policies, and ru... and Multi-Stakeholder ForumRegular dialogue between government and civil society is a core element of OGP participation. It builds trust, promotes joint problem-solving, and empowers civil society to influence the design, imple... to oversee the OGP process. The Steering Committee includes government and civil society representatives chosen from the broader Multi-Stakeholder Forum based on their responsibility for commitments in the current action plan. The co-creation processCollaboration between government, civil society and other stakeholders (e.g., citizens, academics, private sector) is at the heart of the OGP process. Participating governments must ensure that a dive... continues to include the same set of civil society organizations based in Monrovia. This is reflected by the action plan, in which half of the commitments are nearly identical to those in the previous plan. The Secretariat made efforts to reach a broader audience through sensitization and radio sessions. The IRM recommends that the Secretariat seek potential partners beyond the capital and use radio outreach to collect input from the public throughout co-creation and implementation.
Implementation in Context
The COVID-19 pandemic pulled government attention and funding away from implementation of the action plan. Social distancing restrictions caused the Steering Committee and Multi-Stakeholder Forum discussions to be held online and over WhatsApp. Additionally, conflict around the leadership structure at the Liberia Anti-Corruption Commission inhibited implementation of Commitment 4.
[1] “Liberia Action Plan Review 2020-2022,” Open Government Partnership, https://www.opengovpartnership.org/documents/liberia-action-plan-review-2020-2022/.

Leave a Reply