The Action Plans
Access the full 2021 action plans of the OGP Local members included in this analysis:
Introduction
The Open Government Partnership (OGP) provides an opportunity for government and civil society reformers to make governments more transparent, inclusive, participatory, and accountable. Working together, government and civil society co-create action plans with concrete commitments across a variety of sectors.
About OGP Local
In 2016, OGP launched a subnational pilot program that consisted of 15 local members. Five additional local members joined in 2018. The early successes of these “pioneer” members’ action plans has led OGP Local to expand even further. Fifty-six local jurisdictions are making their first OGP action plans in 2021, bringing the total number of OGP local members to 76.
This page summarizes findings – by policy area or approach – from the 36 action plans submitted by OGP Local members between July 1, 2021 and October 1, 2021. Findings will be updated in 2022 after more 2021 local action plans have been submitted.
Cross-Cutting Takeaways
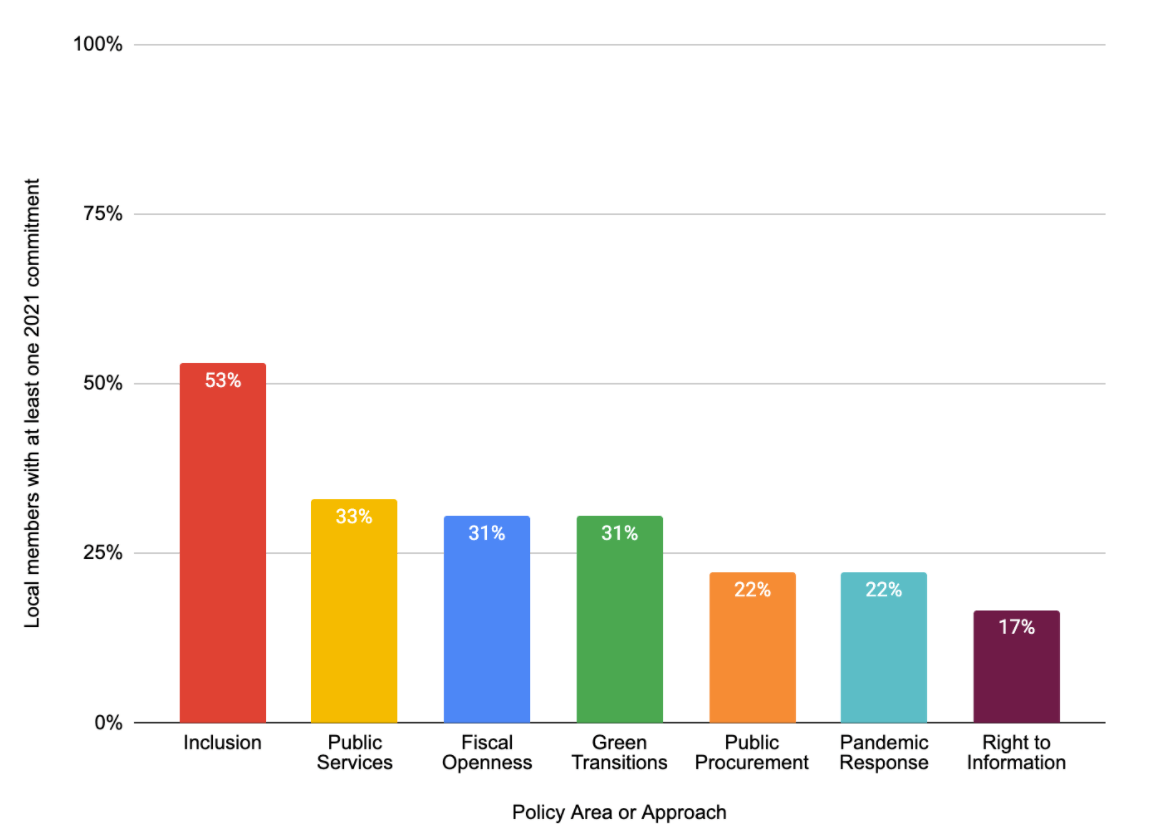
- Making diverse commitments: Local members have made commitments across 15 different policy areas tracked by OGP, ranging from the development of guidance on the government use of artificial intelligence in Ontario, Canada to the creation of public consultation mechanisms in Vinnytsia, Ukraine and Glasgow, United Kingdom (see Figure 1).
- Ensuring opportunities for participation: Nearly half of 2021 local commitments include an element of public participation. In comparison, 40 percent of commitments made by national OGP members in 2020 involved public participation.
- Opening data: Over 20 percent of 2021 local commitments involve publishing data in an open format. Environment and climate, right to information, and fiscal openness commitments most commonly include open data elements.
In this Analysis
|
Featured Policy Areas and Approaches |
Figure 1. Popular Policy Areas in 2021 Local Action Plans
Inclusion is the most popular approach; over half of 2021 local action plans include at least one inclusion-related commitment. Other popular policy areas include public services, fiscal openness, and green transitions.

Inclusion
Societies with greater political and economic equality demonstrate higher sustained rates of growth and lower poverty rates over time. The COVID-19 pandemic, however, has revealed deep disparities and negatively impacted many already-marginalized groups. As an open government approach, inclusion involves reaching out to groups that are traditionally marginalized (such as women, those across the gender and sexual identity spectrum, indigenous and disability communities) and making sure they have access to government-held information and that they can influence decisions. Pioneer OGP Local members made more inclusion-related commitments, on average, than national members. Inclusion continues to be a popular approach among local members, as half of local members with 2021 action plans have made a commitment related to inclusion.
Commitment Examples:
- Khoni, Georgia plans to adopt legislation mandating the participation of persons with disabilities in all future urban development projects to ensure accessibility needs are met.
- Plateau, Nigeria committed to set up a Gender and Equal Opportunities Commission that will work to achieve greater participation of women in decision-making positions, reduce gender-based violence, and reduce discrimination based on gender or marital status.
- Other commitments: Buenos Aires, Argentina; South Cotabato, Philippines; Córdoba (Province), Argentina
Public Services
Improving transparency and engaging citizens at the local level can greatly improve public service quality, especially since local governments deliver many or most public services. One-third of local members with 2021 action plans have made a commitment related to public service delivery. Specifically, these commitments apply open government principles across the education, health, and water & sanitation sectors.
Commitment Examples:
- Bogotá, Colombia will improve public involvement in health services by co-creating health initiatives with citizens and providing better access to health-related information.
- Shama, Ghana committed to involve citizens, along with water service providers and government leaders, in improving the quality of water and sanitation services, in hopes of making clean water accessible to all communities.
- Other commitments: Brebes, Indonesia; Makueni, Kenya; West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia; Tirana, Albania

Fiscal Openness
Citizens have a right to know and have a voice in how their local governments are getting money (through taxes, fees, etc.), what is being prioritized for spending, and whether the money is being used effectively. Fiscal openness was a major area of success among pioneer OGP Local members; one-third of their commitments in this area showed strong early results, and 80 percent were highly ambitious according to the IRM. Nearly one-third of local members with 2021 action plans have made a commitment related to fiscal openness. Two-thirds of these commitments include participatory elements.
Commitment Examples:
- Abuja, Nigeria will work to increase citizens’ awareness of the budget cycle and provide opportunities for citizen input on budget priorities.
- Ozurgeti, Georgia committed to making the approval process for the 2022 fiscal year budget more inclusive for citizens through a series of public meetings.
- Other commitments: Basque Country, Spain; Osasco, Brazil

Green Transitions
Governments have an important opportunity to shift toward more sustainable investments as the world looks to grow its economy in a way that is better for people and their environment. Nearly one-third of local members with 2021 action plans have made a commitment related to green transitions. Commitments range from responding to the consequences of climate change to creating more green spaces and environmentally-friendly infrastructure.
Commitment Examples:
- Gwangju, South Korea committed to increasing participatory decision-making in climate change management policy through conducting educational activities and collecting opinions on policy proposals from citizens.
- Santo Domingo de los Tsáchilas, Ecuador will fight against deforestation processes by publishing open data on the inventory of forest species, creating an online system to accept citizens’ complaints of environmental impacts, and co-creating an environmental control policy.
- Other commitments: Khmelnytskyi, Ukraine; Mendoza, Argentina; Banská Bystrica, Slovak Republic; Banggai, Indonesia

Public Procurement
Ensuring transparency in the public procurement process increases competition, enables greater citizen monitoring, and ensures better value for money. Within these procurement processes, open contracting involves disclosure and citizen engagement throughout the entire procurement process. Nearly a quarter of local members with 2021 action plans have made a commitment related to public procurement. In turn, three-quarters of these commitments specifically reference open contracting principles.
Commitment Examples:
- Santa Catarina, Brazil will implement greater transparency of public procurement by training public servants, adding accessibility options within the online procurement portal, and publishing procurement data in an open format.
- Makueni, Kenya committed to publishing project implementation data based on the Open Contracting Data Standard. The procurement portal will be interoperable with Kenya’s national e-procurement system.
- Other commitments: Plateau, Nigeria; Rosario, Argentina; Nandi, Kenya

Pandemic Response
OGP launched the Open Response + Open Recovery campaign in 2020 to emphasize the importance of open government values in creating a strong pandemic response. This is especially critical for local governments, which are responsible for delivering health services and vaccine distribution. Nearly a quarter of local members with 2021 action plans have made a pandemic response-related commitment.
Commitment Examples:
- São Paulo, Brazil committed to publish open data on vaccination rates and hospital infrastructure and prepare a report about the pandemic’s impact on school retention rates.
- Basque Country, Spain will work to identify indicators, measure, and publish open data that shows the impact of the pandemic on municipal services.
- Other commitments: Semarang, Indonesia; West Sumbawa, Indonesia

Right to Information
The legal right to request information from the government helps the public to follow government activity, participate in ensuring better decisions, and hold officials accountable. So far, one-sixth of local members with 2021 action plans have made a commitment related to the right to information. These include commitments related to both the proactive and reactive disclosure of government-held information.
Commitment Examples:
- Tangier – Tetouan – Al-Hoceima, Morocco plans to adopt the national portal of access to information, raise awareness of the right to access information among citizens, and increase the proactive release of information.
- Rosario, Argentina committed to publishing open data on responses to requests for information and improving API tools that facilitate the online access to information portal.
- Other commitments: Aragón, Spain; Santa Catarina, Brazil
